 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsLet P be the point (1, 0) and Q a point on the locus y2 = 8x. The locus of mid point of PQ is
y2 – 4x + 2 = 0
y2 + 4x + 2 = 0
x2 + 4y + 2 =
x2 + 4y + 2 =
The locus of a point P (α, β) moving under the condition that the line y = αx + β is a tangent to the hyperbola 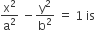
an ellipse
a circle
a parabola
a parabola
D.
a parabola
Tangent to the hyperbola 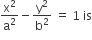
Given that y = αx + β is the tangent of hyperbola
⇒ m = α and a2 m2 – b2 = β2
∴ a2 α2 – b2 = β2
Locus is a2 x2 – y2 = b2 which is hyperbola.
If the circles x2 + y2 + 2ax + cy + a = 0 and x2 + y2 – 3ax + dy – 1 = 0 intersect in two distinct points P and Q then the line 5x + by – a = 0 passes through P and Q for
exactly one value of a
no value of a
infinitely many values of a
infinitely many values of a
A circle touches the x-axis and also touches the circle with centre at (0, 3) and radius 2. The locus of the centre of the circle is
an ellipse
a circle
a hyperbola
a hyperbola
If a circle passes through the point (a, b) and cuts the circle x2 + y2 = p2 orthogonally, then the equation of the locus of its centre is
x2 + y2 – 3ax – 4by + (a2 + b2 – p2 ) = 0
2ax + 2by – (a2 – b2 + p2 ) = 0
x2 + y2 – 2ax – 3by + (a2 – b2 – p2 ) = 0
x2 + y2 – 2ax – 3by + (a2 – b2 – p2 ) = 0
An ellipse has OB as semi-minor axis, F and F′ its focii and the angle FBF′ is a right angle. Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is
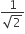
1/2
1/4
1/4
If the pair of lines ax2 + 2(a + b)xy + by2 = 0 lie along diameters of a circle and divide the circle into four sectors such that the area of one of the sectors is thrice the area of another sector then
3a2 – 10ab + 3b2 = 0
3a2 – 2ab + 3b2 = 0
3a2 + 10ab + 3b2 = 0
3a2 + 10ab + 3b2 = 0
If a circle passes through the point (a, b) and cuts the circle x2 +y2= 4 orthogonally, then the locus of its centre is
2ax +2by + (a2 +b2+4)=0
2ax +2by - (a2 +b2+4)=0
2ax -2by - (a2 +b2+4)=0
2ax -2by - (a2 +b2+4)=0
