263.
Find the Cartesian as well as the vector equation of the planes passingВ through the intersection of the planesВ  В which are at unit distance from the origin.В
В which are at unit distance from the origin.В
The equation of first plane is
В В В В В В В В В В 
or В В В В 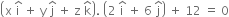

The equation of second plane is
В В В В В В 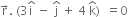
or В В В В В 
or В В В В В В 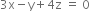 В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В ...(2)
В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В ...(2)
The equation of any plane through the intersection of planes (1) and (2) is
(x + 3 y + 6) + k (3 x – y + 4 z) = 0
or (3 k + l).x + (–k + 3)y + 4 kz + 6 = 0    ...(3)
From given condition,
perpendicular distance of origin (0, 0, 0) from plane (3) = 1
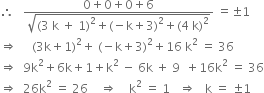 Taking k = 1, from (3), we get,
Taking k = 1, from (3), we get,
В В
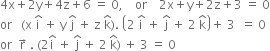 Taking k = – 1, from (3), we get,
Taking k = – 1, from (3), we get,
В В В В В В



The required cartesian equations are
2x + y + 2z + 3 = 0, x – 2y + 2z — 3 = 0
andВ
В vector equations are

77 Views
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type