 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet O be the origin and OA = a, OB = b, OC = c
∴ equation of plane passing through A, B and C is
![]()
or ![]()
From the given condition, 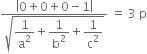
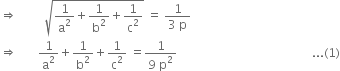
Now A, B, C are (a, 0, 0), (0, b, 0), (0, c, 0) respectively.
Let (x1 , y1 , z1 ) be the centroid of ΔABC.![]()
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsDistance between the two planes: 2x + 3y + 4z = 4 and 4x + 6y + 8 z = 12 is
2 units
4 units
8 units
8 units
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type