 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA body of mass 2m moving with velocity v makes a head on elastic collision with another body of mass m which is initially at rest. Loss of kinetic energy of the colliding body (mass 2m) is
1/9 of its initial kinetic energy
1/6 of its initial kinetic energy
8/9 of its initial kinetic energy
1/2 of its initial kinetic energy
Displacement x (in meters), of body of mass 1 kg as a function of time t, on a horizontal smooth surface is given as x = 2t2 . The work done in the first one second by the external force is
1 J
2 J
4 J
8 J
Under the action of a constant force, a particle is experiencing a constant acceleration. The power is
zero
positive constant
negative constant
increasing uniformly with time
CO− ion moving with kinetic energy of 20 keV dissociates into O− and C which move along the parent ion direction. Assuming no energy is released during dissociation, the kinetic energy of the daughters (K.E)O and (K.E)C are related as
(K.E)O− = (K.E)C
(K.E)O− / (K.E)C = 16/12
(K.E)O− / (K.E)C = 12/16
(K.E)O− / (K.E)C = 16/28
The work-energy theorem states that the change in
kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force
kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done by one of the forces acting on it.
potential energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force
potential energy of a particle is equal to the work done by one of the forces acting on it
A car of masses 1500 kg is lifted up a distance of 30 m by crane A in 0.5 minutes. The second crane B does the same job in 1 minute. The ratio of their powers is
1 : 2
2 : 1
1 : 1
1 : 4
If the average kinetic energy of a molecule of a hydrogen gas at 300 K is E, then the average kinetic energy of a molecule of a nitrogen gas at the same temperature is
7 E
E/14
E
E/7
A cricket ball is hit at an angle of 30° to the horizontal with a kinetic energy E. Its kinetic energy when it reaches the highest point is
0
A spring with force constant k is initially stretched by x1. If it is further stretched by x2, then the increase in its potential energy is
A force Fx acts on a particle such that its position x changes as shown in the figure.
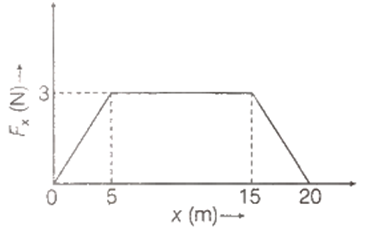
The work done by the particle as it moves from x = 0 to 20 m is
37.5 J
10 J
45 J
22.5 J
