 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFor isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, the correct combination of the thermodynamic parameters will be
U = 0; Q = 0; W ≠ 0 and H ≠ 0
U ≠ 0; Q ≠ 0; W ≠ 0 and H = 0
U = 0; Q ≠ 0; W = 0 and H ≠ 0
U = 0; Q ≠ 0; W ≠ 0 and H = 0
The condition of spontaneity of a process is
lowering of entropy at constant temperature and pressure
lowering of Gibbs free energy of system at constant temperature and pressure
increase of entropy of system at constant temperature and pressure
increase of Gibbs free energy of the universe at constant temperature and pressure
Which of the following is correct?
Evaporation of water causes an increase in disorder of the system
Melting of ice causes a decrease in randomness of the system
Condensation of steam causes an increase in disorder of the system
There is practically no change in the randomness of the system when water is evaporated
Given, G°=-nFE°cell and G° = -RT ln k. The value of n = 2 will be given by the slope of which line in the figure
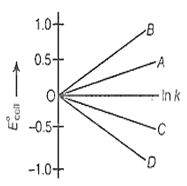
OA
OB
OC
OD
For the given reaction,
H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2H+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq); = -262.4 kJ
The value of free energy of formation () for the ion Cl-1 (aq), therefore will be
-131.2 kJ mol-1
+131.2 kJ mol-1
-262.4 kJ mol-1
+262.4 kJ mol-1
Find the correct equation
E2 - E1 - H2 + H1 = n2RT - n1RT
E2 - E1 - H2 - H1 = n2RT - n1RT
H2 - H1 - E2 + E1 = n2RT - n1RT
H2 - H1 - E2 - E1 = n2RT - n1RT
The standard enthalpy of formation of H2O (l) and Fe2O3 (s) are respectively -286 kJ mol-1 and -824 kJ mol-1. What is the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction?
Fe2O3 (s) + 3H2 (g) → 3H2O (l) + 2Fe (s)
-538 kJ mol-1
+538 kJ mol-1
-34 kJ mol-1
+34 kJ mol-1
Calculate H in kJ for the following reaction:
C (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
Given that,
H2O (g) + C (g) → CO (g) + H2 (g) ; H = +131 kJ
CO (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g); H = -282 kJ
H2 (g) + O2 (g) → H2O (g); H = -242 kJ
-393
+393
+655
-655
To convert 94 g of ice at 0°C into 94g of vapour at 100° C, the quantity of coal (90% carbon) required is : (ΔHc of carbon = -94 k cal mol-1);latent heat of fusion = + 80 cal per gm; latent heat ofvaporisation=+ 540 cal per gm; specificheat of water = 1 cal per gm per °C).
94g
80g
9.4g
9.6 g
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes.
| List I | List II |
| A. Spontaneous process | 1 Δh < 0 |
| B. Exothermic process | 2. Heat of reaction |
| C. Enthalpy at constant pressure | 3. ΔG < 0 |
| D. Cyclic process | 4. ΔU= 0, ΔH = 0 |
A B C D
4 2 1 3
A B C D
3 1 2 4
A B C D
1 3 4 2
A B C D
1 2 3 4
