 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following pairs of hormones are not antagonistic (having opposite effects) to each other?
| Insulin | Glucagon |
| Aldosterone | Atrial Natriuretic Factor |
| Relaxin | Inhibin |
| Relaxin | Inhibin |
A pregnant female delivers a baby, who suffer from stunted growth, mental retardation low intelligence quotient and abnormal skin. This is the result of
deficiency of iodine in diet
low secretion of growth hormone
cancer of the thyroid glad
cancer of the thyroid glad
Which of the following statement is correct in relation to the endocrine system?
Adenohypophysis is under the direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus.
Organs in the body like gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney and live
Non-nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that acts as intercellular messengers are known as hormones.
Non-nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that acts as intercellular messengers are known as hormones.
Which one of the following hormones is not involved in sugar metabolism?
Cortisone
Aldosterone
Insulin
Insulin
Which one of the following hormones though synthesised elsewhere, is stored and released by the master gland?
Antidiuretic hormone
Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Prolactin
A person entering an empty room suddenly finds a snake right in front on opening the door. Which one of the following is likely to happen in his neurohormonal control system?
Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal medulla
Neurotransmitters diffuse rapidly across the cleft and transmit a nerve impulse
Hypothalamus activates the parasympathetic division of brain
Hypothalamus activates the parasympathetic division of brain
Which one of the following pairs of hormones are the examples of those that can easily pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor inside it(mostly the nucleus)
Insulin and glucagon
Thyroxin and insulin
Somartostatin and oxytocin
Somartostatin and oxytocin
What is correct to say about the hormone action in humans?
Glucagon is secreted by 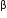 -cells of Islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis
-cells of Islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis
Secretion of thymosine is stimulated with ageing
In females, FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
In females, FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
Identify the hormone with its correct matching of source and function.
Oxytocin - posterior pituitary, growth and maintenance of mammary glands.
Melatonin - pineal gland, regulates the normal rhythm of sleep-wake cycle
Progesterone - corpus luteum, stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs
Progesterone - corpus luteum, stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs
Fight or flight reactions cause activation of
the parathyroid glands, leading to increased metabolic rate
the kidney, leading to suppression of reninangiotensin - aldosterone pathway
the adrenal medulla, leading to increased secretion epinephrine and norepinephrine
the adrenal medulla, leading to increased secretion epinephrine and norepinephrine
