Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange the following in the decreasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solutions:
CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3 N and NH3
A 1.00 molar aqueous solution of trichloroacetic acid (CCl3COOH) is heated to its boiling point. The solution has the boiling point of 100.180C. Determine the van’t Hoff factor for trichloroacetic acid. (Kb for water = 0.512 kg mol-1)
Define the following terms:
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor
(iv) Ideal solution
What do you understand by the ‘order of a reaction’? Identify the reaction order from each of the following units of reaction rate constant:
(i) L-1 mol-1
(ii) L mol-1 s-1
Name the two groups into which phenomenon of catalysis can be divided. Give an example of each group with the chemical equation involved.
What is meant by coagulation of a colloidal solution? Describe briefly any three methods by which coagulation of lyophobic sols can be carried out.
Describe the principle involved in each of the following processes.
(i) Mond process for refining of Nickel.
(ii) Column chromatography for purification of rare elements.
Mond process for refining of Nickel is based on the principle that nickel is heated in the presence of carbon monoxide to form nickel tetracarbonyl, which is a volatile complex.
Ni + 4CO ![]() Ni(CO)4
Ni(CO)4
(Nickel tetracarbonyl)
Then, the obtained nickel tetracarbonyl is decomposed by subjecting it to a higher temperature (450 - 470 K) to obtain pure nickel metal.
Ni(CO)4 ![]() Ni + 4CO
Ni + 4CO
(Nickel tetracarbonyl) nickel
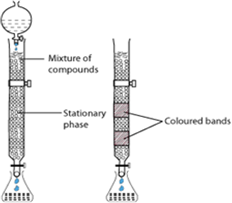
(ii) Column chromatography is based on the principle that different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent. In it, there are two phases: mobile phase and stationary phase. The stationary phase is immobile and immiscible example Silica gel(SiO2) , Alumina gel(Al2O3) . Al2O3 column is usually used as the stationary phase in column chromatography. The mobile phase may be a gas, liquid, or supercritical fluid in which the sample extract is dissolved.
Then, the mobile phase is forced to move through the stationary phase. The component that is more strongly adsorbed on the column takes a longer time to travel through it than the component that is weakly adsorbed. The adsorbed components are then removed (eluted) using a suitable solvent (eluent).