 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type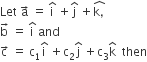
 ┬Ācoplanar.
┬Ācoplanar. ┬Ācoplanar.
┬Ācoplanar.
Find the area bounded by the circle x2 + y2 = 16 and the line ŌłÜ3y=x in the first quadrant, using integration.
The area of the region bounded by the circle, x2+y2=16, x=ŌłÜ3y, and the x-axis is the area OAB.
Solving x2+y2=16 and x=ŌłÜ3y, we have
(ŌłÜ3y)2+y2=16
ŌćÆ3y2+y2=16
ŌćÆ4y2=16
ŌćÆy2=4
ŌćÆy=2
(In the first quadrant, y is positive)
When y = 2, x = 2ŌłÜ3
So, the point of intersection of the given line and circle in the first quadrant is (2ŌłÜ3,2).
The graph of the given line and circle is shown below:
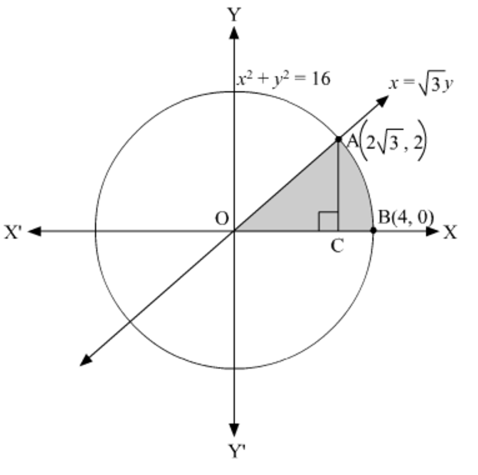
Required area = Area of the shaded region = Area OABO = Area OCAO + Area ACB
Area OCAO = 12├Ś2ŌłÜ3├Ś2=2ŌłÜ3 sq units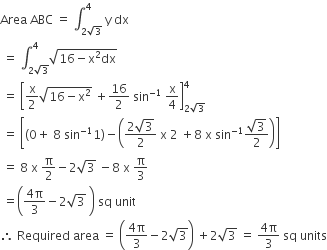
Using integration, find the area of region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (ŌĆō2, 1), (0, 4) and (2, 3).
