 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) (i) 'Two independent monochromatic sources of light cannot produce a sustained interference pattern'. Give reason.
(ii) Light waves each of amplitude 'a' and frequency 'ω', emanating from two coherent light sources superpose at a point. If the displacements due to these waves is given by y1 = a cos ωt and y2 = a cos(ωt + ϕ) where ϕ is the phase difference between the two, obtain the expression for the resultant intensity at the point.
(b) In Young's double slit experiment, using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point where path difference is λ/3.
(a) How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarized light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarized?
(b) A beam of unpolarized light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarized, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.(a) State briefly the processes involved in the formation of p-n junction explaining clearly how the depletion region is formed.
(b) Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
(i) Forward biasing
(ii) Reverse biasing
How these characteristics are made use in rectification?
(a) Differentiate between three segments of a transistor on the basis of their size and level of doping.
(b) How is a transistor biased to be in active state?
(c) With the help of necessary circuit diagram, describe briefly how n-p-n transistor in CE configuration amplifies a small sinusoidal input voltage. Write the expression for the ac current gain.On the basis of size and level of doping,
(a)
Emitter (E) - Emitter is heavily doped and is the left hand side thick layer of the transistor.
Base (B) - It is the central thin layer of the transistor, which is lightly doped.
Collector (C) - It is the right hand side thick layer of the transistor, which is moderately doped.
(b)
There are two conditions for a transistor to be into an active region.
1. The input circuit should be forward biased by using a low voltage battery.
2. The output circuit should be reverse biased by using a high voltage battery.
(c)
n-p-n Transistor as an amplifier:
The input circuit is forward biased by using a low voltage battery. Hence, the resistance of the input circuit is small. The output circuit is reverses biased using a high voltage battery. Hence, the resistance of the output circuit is large.
The operating point is fixed in the middle of its active region.
The output is taken between the collector and the ground.
Applying Kirchhoff’s law to the output loop:
VCC = VCE + ICRC
If Vc is the collector voltage then,
Vc = VCE − ICRC ... (A)
When the input signal voltage is fed to the emitter base circuit, it will change the emitter voltage and hence to the emitter current, which in turn will change the collector current. Due to this the collector voltage VC will vary in accordance with relation (A). This variation in collector voltage appears as the amplified output.
VBB = VBE + IBRB
Here, vi ≠ O
Then, VBB + vi = VBE + IBRB + ΔIB (RB + ri)
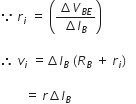 ; is the required expression for current gain.
; is the required expression for current gain.
