 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type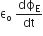 , where
, where  is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
Explain the terms (i) Attenuation and (ii) Demodulation used in Communication System.
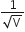 , where V is the is accelerating potential for two particles A and B, carrying the same charge but different masses m1 and m2 (m1 > m2). Which one of the two represents a particle of smaller mass and why?
, where V is the is accelerating potential for two particles A and B, carrying the same charge but different masses m1 and m2 (m1 > m2). Which one of the two represents a particle of smaller mass and why? 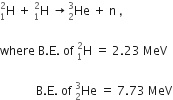
(a) Explain any two factors that justify the need of modulating a low-frequency signal.
(b) Write two advantages of frequency modulation over amplitude modulation.
i) The function of three segments of a transistor are:
Emitter: Emits the majority charge carriers
Collector: Collects the majority charge carriers
Base: Base provides the interaction between the collector and the base
ii) An n-p-n transistor is as shown below: 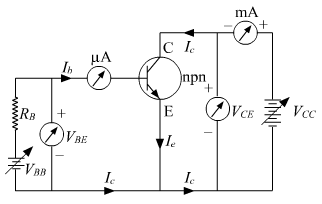
Input characteristics: The variation between the base current and the base-emitter voltage is obtained. Input characteristics is used to find input dynamic resistance of the transistor as it is represented by the slope.
Output characteristics: A graph representing the variation of the collector current and emitter voltage is obtained, keeping base current fixed. The slope fo the output characteristic graph gives us the output dynamic resistance.
