 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeTwo electric bulbs P and Q have their resistances in the ratio of 1: 2. They are connected in series across a battery.Find the ratio of the power dissipation in these bulbs.
Let ratio be x
Rp = x (Resistance of bulb P)
Rq = 2x (Resistance of bulb Q)
We know, P = VI = V.V/R
A 10 V cell of negligible internal resistance is connected in parallel across a battery of emf 200 V and internal resistance 38 Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of current in the circuit.
In a potentiometer arrangement for determining the emf of a cell, the balance point of the cell in open circuit is 350 cm. When a resistance of 9 ohm is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 300 cm. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
Four point charges Q, q, Q and q are placed at the corners of a square of side ‘a’ as shown in the figure
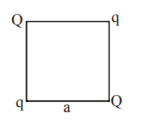
Find the
(a) resultant electric force on a charge Q,
(b) the potential energy of this system.
Three point charges q, – 4q and 2q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side ‘l’ as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the magnitude of the resultant electric force acting on the charge q.
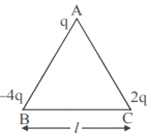
(b) Find out the amount of the work done to separate the charges at infinite distance.
Using the concept of free electrons in a conductor, derive the expression for the conductivity of a wire in terms of number density and relaxation time. Hence obtain the relation between current density and the applied electric field E.
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 6 J/T is aligned at 60° with a uniform external magnetic field of 0.44 T. Calculate (a) the work done in turning the magnet to align its magnetic moment (i) normal to the magnetic field, (ii) opposite to the magnetic field, and (b) the torque on the magnet in the final orientation in case (ii).
An iron ring of relative permeability μr has windings of insulated copper wire of n turns per metre. When the current in the windings is I, find the expression for the magnetic field in the ring.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0.9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
