 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA capacitor of 8 Fis connected as shown in the figure. Charge on the plates of the capacitor
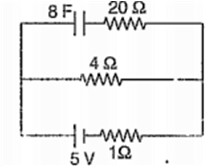
32 C
40 C
0 C
80 C
Four metal plates are arranged as shown in the figure. Capacitance between X and Y (A ➔ Area of each plate, d ➔ distance between the plates) is
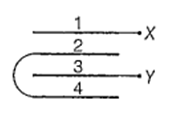
Mobility of free electrons in a conductor is
directly proportional to electron density
directly proportional to relaxation time
inversely proportional to electron density
inversely proportional to relaxation time
Variation of resistance of the conductor with temperature is as shown
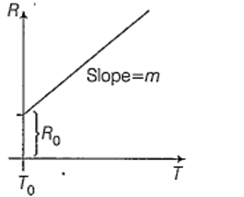
The temperature coefficient (α) of the conductor is
mR0
m2R0
Effective resistance between A and B in the following circuit 
10 Ω
20 Ω
5 Ω
A.
10 Ω

It is a balanced Wheatstone's bridge network with the resistances being 10 Ω each.
∴ Reff AB = 10 Ω
Two heating coils of resistances 10 Ω and 20 Ω are connected in parallel and connected to a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 1 Ω. The power consumed by them are in the ratio
1 : 4
1 : 3
2 : 1
4 : 1
A proton is projected with a uniform velocity v along the axis of a current-carrying solenoid, then
the proton will be accelerated along the axis
the proton path will be circular about the axis
the proton move along helical path
the proton will continue to move with velocity v along the axis
In the cyclotron, as radius of the circular path of the charged particle increases (ω = angular velocity, v = linear velocity)
both ω and v increase
ω only increases, v remains constant
v increases, ω remains constant
v increases, ω decreases
