 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA heating element of resistance r is fitted inside an adiabatic cylinder which carries a frictionless piston of mass m and cross-section A as shown in diagram. The cylinder contains one mole of an ideal diatomic gas. The piston current flows through the element such that the temperatures rises with time t as ΔT = αt + βt2 ? (α and β are constants), while pressure remains constant. The atmospheric pressure above the piston is P0. Then
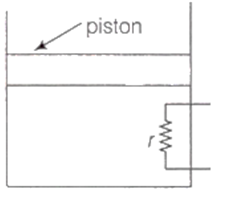
he rate of increase in internal energy is
the current flowing in the element is
the piston moves upwards with constant acceleration
the piston moves upwards with constant speed
A.
he rate of increase in internal energy is
We know that
Internal energy,
Differentiate with respect to t
So, the rate of increase in internal energy is ,and the piston moves upwards with constant acceleration.
Three capacitors 3 µF, 6 µF and 6 µF are connected in series to a source of 120 V. The potential difference, in volt, across the 3 µF capacitor will be
24
30
40
60
A galvanometer having internal resistance 10 Ω requires 0.01 A for a full scale deflection. To convert this galvanometer to a voltmeter of full-scale deflection at 120 V, we need to connect a resistance of
11990 Ω in series
11990 Ω in parallel
12010 Ω in series
12010 Ω in parallel
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then disconnected from the charging battery. If the plates are now moved farther apart by pulling at them by means of insulating handles, then
the energy stored in the capacitor decreases
the capacitance of the capacitor increases
the charge on the capacitor decreases
the voltage across the capacitor increases
An electron in a circular orbit ofradius 0.05 nm performs 1016 revolutions per second. The magnetic moment due to this rotation of electron is (in Am2)
2.16 × 10-23
3.21 × 10-22
3.21 × 10-24
1.26 × 10-23
A very small circular loop of radius a is initially (at t = 0) coplanar and concentric with a much larger fixed circular loop of radius b. A constant current I flows in the larger loop. The smaller loop is rotated with a constant angular speed ω about the common diameter. The emf induced in the smaller loop as a function of time t is
An infinite sheet carrying a uniform surface charge density σ lies on the xy-plane. The work done to carry a charge q from the point to the point (where a is a constant with the dimension of length and ε0 is the permittivity of free space) is
The intensity of magnetization of a bar magnet is 5.0 x 104 Am-1.The magnetic length and the area of cross section of the magnet are 12 cm and 1cm2 respectively. The magnitude of magnetic moment of this bar magnet is (in SI unit)
0.6
1.3
1.24
2.4
A proton of mass m and charge q is moving in a plane with kinetic energy E. If there exists a uniform magnetic field B, perpendicular to the plane of the motion, the proton will move in a circular path of radius
In which of the following phenomena, the heat waves travel along straight lines with the speed of light ?
Thermal conduction
Forced convection
Natural convection
Thermal radiation
