
Draw the electron dot structures for:
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) H2S
(c) propanone
(d)F2’
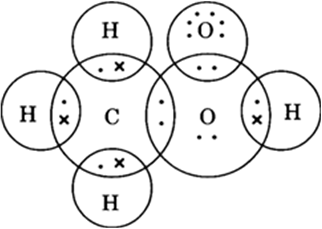
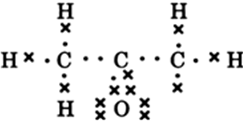
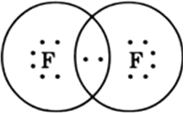
B.
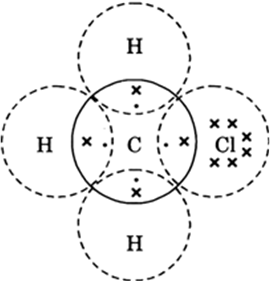
the fuel is not burning completelyExplain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
|
Teat |
Ethanol |
Ethanoic acid |
|
1. Litmus test 2. Sodium bicarbonate 3. Sodium metal test |
No change in colour of litmus solution. No brisk effervescence. H2 is given out with effervescence. |
Blue litmus solution turns red. Brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2. H2 is produced but no effervescence. |
A homologous series is a group of compounds which contains the same functional group but different chain lengths. Thus, these have the same chemical properties but different physical properties.
Example:
CH3OH
C2H5OH
C3H7OH
C4H9OH
Above are members of the same homologous series having different chain length and same functional group.
