
What is meant by hybridization of atomic orbitals? Describe the shapes of sp, sp2, sp3 hybrid orbitals.
The phenomenon of mixing of orbitals of the same atom with a slight difference in energies so to redistribute their energies and give new orbitals of equivalent energy and shape. It is called as hybridization.
These hybrid orbitals have minimum repulsion between their electron pairs and thus, are more stable. Hybridization helps indicate the geometry of the molecule.
Sp3 hybridisation; This type of hybridization involves the mixing of one orbital of s- sub level or three orbitals of the p-sublevel of the valence shell to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals of equivalent energies and shape. Each sp3 hybrid orbital has 25% s character and 75% p-character. These hybridised orbitals tend to lie as apart in space as possible so that repulsive interaction between them are minimum. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals are directed towards the four corners of a tetrahedron. The angle between the sp3 hybrid orbitals is 109.5.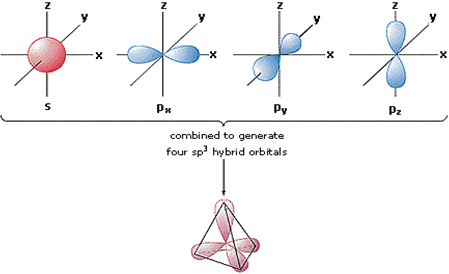
Sp2 hybridisation: This type of hybridization involves the mixing of one orbital of s- sublevel and two orbitals of p-sublevel of the valence shell to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. These sp2 hybrid orbitals lie in a plane and are directed towards the corners of the equilateral triangle.
Each sp2 hybrid orbitals has one-third s- character and two -third p- character. sp2 hybridization is also called trigonal hybridisation.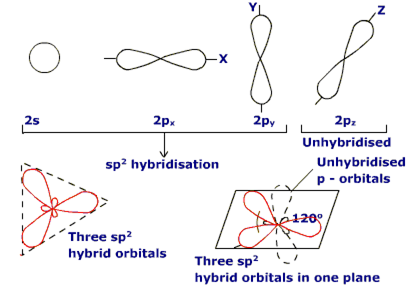
sp-hybridisation: This type of hybridization involves the mixing of one orbital of the s-sublevel and one p-sublevel of the valence shell of the atom to form two sp- hybridised orbitals of equivalent shapes and energies. These sp hybridised orbitals are oriented in space at an angle of 180.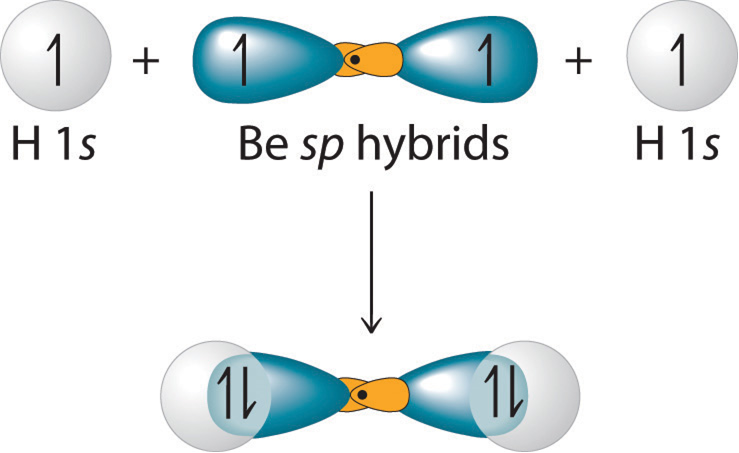
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
(a) C2H2 (b) C2H4
(a) C2H2
H – C ≡ C – H
Number of sigma bonds = 3
Number of  bonds = 2
bonds = 2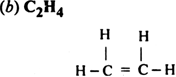
Number of sigma bonds = 5
Number of  bonds = 1
bonds = 1
What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Illustrate by giving one example of each type.
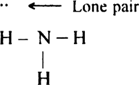
Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
If two different atoms are linked to each other by a covalent bond,then the shared electron pair will not lie in the centre because the bonding atoms differ in electronegativities.Such a bond is called as polar covalent bond.For in NaCl , chlorine is more electronegative than sodium. Hence it will have more control over the shared pair of electrons & will develop a partial negative charge & sodium will acquire partial positive charge & a polar covalent bond is formed. Greater the difference in electronegativity of bonding atoms more will be the polarity of the bond.
Consider two hydrogen atoms A and B with electron eA and eB respectively. HArepresents the nucleus of hydrogen atom A and HB represents the nucleus of hydrogen atom B.
When the two hydrogen atoms approach each other, the following two forces come into existence:
(a) Attractive interactions in between:
(i) the nucleus HA an electron eB and
(ii) the nucleus HB and electron eA
(b) Repulsive interactions in between:
(i) electron eA and electron eB and
(ii) nucleus HA and nucleus HB.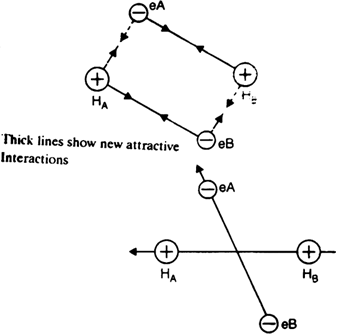
Since attractive forces overpower the repulsive forces, as a result, the enthalpy of the system decreases and a molecule of hydrogen is formed.
Enthalpy diagram: When two hydrogen atoms are at an infinite distance from each other, there is no interaction between them and therefore, the enthalpy of the system is assumed to be zero in this state (stage-A). As the two atoms start coming closer to each other, the potential enthalpy continues to decrease (stage B). Ultimately a stage is reached when the enthalpy of the system becomes minimum and hydrogen atoms are said to be bonded together to form a stable H2 molecule (state C).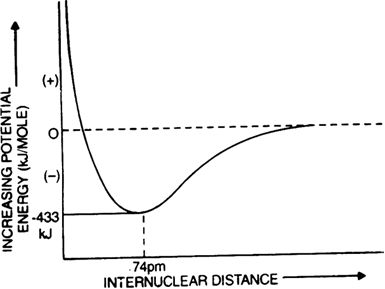
The internuclear distance r0 between two hydrogen atoms at this stage is referred to as bond length. In the case of the hydrogen molecule, the bond length is 74 pm. It should be noted that two hydrogen atoms can not be brought at a distance lesser than rQ (i.e. 74 pm) because the potential enthalpy of the system increases and curve shows an upward trend (dotted lines) and molecule becomes unstable.
