Two identical cells, each of emf E, having negligible internal resistance, are connected in parallel with each other across an external resistance R. What is the current through this resistance?
Internal resistance of the circuit is negligible.
So, total resistance is R.
Therefore, current across the circuit is given by, 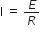
Assume that each diode as shown in the figure has a forward bias resistance of 50 Ω and an infinite reverse bias resistance. The current through the resistance 150 Ω is
0.66 A
0.05 A
Zero
0.04 A
D.
0.04 A
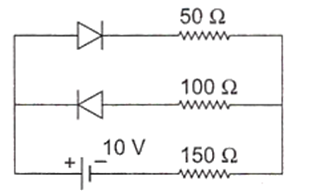
The circuit is
As the lower diode attached to 100 Ω resistance is in reversed biased so, it is non- conducting.
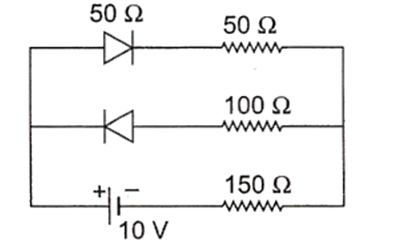
Now, the circuit can be redrawn as,
∴ Current through the circuit,
A metal wire of circular cross-section has a resistance R1. The wire is now stretched without breaking, so that its length is doubled and the density is assumed to remain the same. If the resistance of the wire now becomes R2 then R2 : R1 is
1 : 1
1 : 2
4 : 1
1 : 4
C.
4 : 1
As we know that,
where, l = length of wire
a = area of cross-section of the wire
and V = volume of the wire R1 ∝ l2
Two cells A and B of emf 2V and 1.5 V respectively, are connected as shown in figure through an external resistance 10 Ω. The internal resistance of each cell is 5 Ω. The potential difference EA and EB across the terminals of the cells A and B respectively are
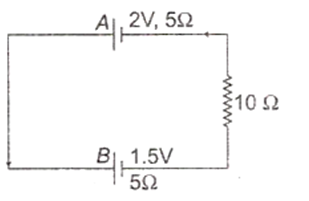
EA = 2.0 V, EB = 1.5 V
EA = 2.125 V, EB = 1.375 V
EA = 1.875 V, EB = 1.625 V
EA = 1.875 V, EB = 1.375 V
C.
EA = 1.875 V, EB = 1.625 V
The figure can be redrawn as
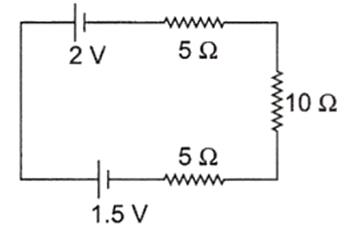
The current through the circuit
The terminal potential difference of the batteries
VA = εA − irA = 2 − 0.025 × 5
= 2 − 0.0125 = 1.875 V
and VB = εB + irB = 1.5 + 0.025 × 5
= 1.5 + 0.0125
= 1.625 V
The current I is in the circuit shown is
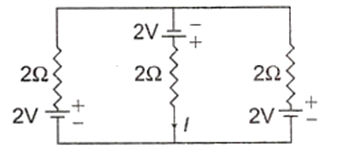
1.33 A
Zero
2.00 A
1.00 A
A.
1.33 A
The circuit diagram can be redrawn as
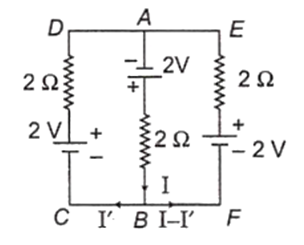
For the loop ABCDA,
+2 − 2I' + 2 − 2I = 0 .......(i)
For the loop ABFEA,
2 − 2I + 2 − 2(I − I') = 0
4 − 2I − 2I + 2I' = 0
4 − 4I + 2I' = 0
2 = 2I − I' ...... (ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
2 = 2I − I' , 2 = I + I'
4 = 3I , I = 4/3 = 1.33 A
