Whether a reaction is of first order or not can be verified by using the analytical methods based on the rate equations. The reagents are allowed to react, the change of concentration is measured at different time intervals. For a first order reaction:
(i) Plot of log [A0]/[A] versus t gives a straight line passing through the origin.
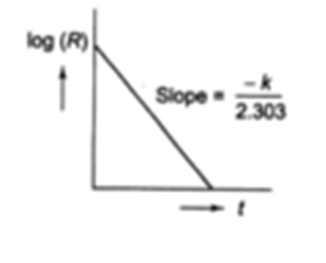
(ii) Plot of log[A] versus t gives a straight line with an intercept log [A]0 and a slope = – k /2.303.
(iii) Plot of [A] versus t is exponential.
(iv) The value of k calculated by using kt = 2.303 log [A]0 / [A] for different time intervals come out to
be same.
(v) The half life period is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
Activated complex is the intermediate compound formed by reactants, which is highly unstable and readily changes into product. Those reactants which possess activation energy and collide in proper orientation can form activated complex which can easily form products.
Lower the activation energy, more easily activated complex will be formed and faster will be the reaction.
Activation energy = energy of activated complex - energy of reactants.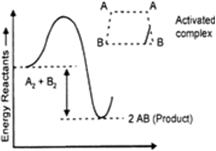
Energy of activation. The minimum energy over average energy which must be gained by the molecules before they could react to form products is called the energy of activation. It is denoted by Ea.
According to the Arrhenius theory, activation energy is independent of temperature. However, precise measurements indicate that the activation energy tends to decrease slightly with a rise in temperature.
