 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type1. Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
2. Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
3. Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place.
4. Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
1. Synapsis
2. Bivalent
3. Chiasmata.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Discuss with your teacher about.
1. haploid insects and lower plants where cell division occurs, and
2. Some haploid cells in higher plants where cell division does not occur.
1. Number of chromosomes per cell.
2. Amount of DNA content (C) per cell.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeInterphase is the resting stage of the cell cycle. It covers 95% of the total duration of a cell cycle. It involves a series of changes that prepare a cell for division. It is the period during which the cell experiences growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. Interphase is divided into three phases.
(i) G1 phase
(ii) S phase
(iii) G2 phase
G1 phase - It is the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication. It is the stage during which the cell grows and prepares its DNA for replication. In this phase, the cell is metabolically active but there is no replication of the DNA.
S phase - It is known as the synthesis phase as it is the stage during which DNA synthesis occurs. In this phase, the amount of DNA (per cell) doubles, but the chromosome number remains the same.
G2 phase - In this phase, the cell continues to grow and prepares itself for the division. The proteins and RNA required for mitosis are synthesised during this stage.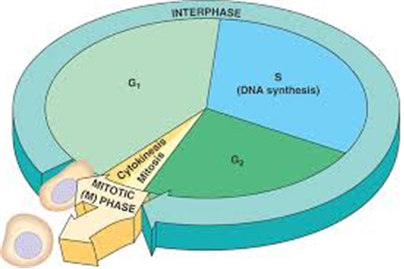
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type