 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
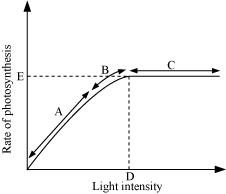
Long Answer TypeFigure 13.10 shows the effect of light on the rate of photosynthesis. Based on the graph, answer the following questions:
(a) At which point/s (A, B or C) in the curve is light a limiting factor?
(b) What could be the limiting factor/s in region A?
(c) What do C and D represent on the curve?
Give comparison between C3 and C4 pathways.
|
C3 pathways |
C4 pathways |
||
|
1. |
The primary acceptor of CO2 is RUBP – a six-carbon compound. |
1. |
The primary acceptor of CO2 is phosphoenol pyruvate – a three-carbon compound. |
|
2. |
The first stable product is 3-phosphoglycerate. |
2. |
The first stable product is oxaloacetic acid. |
|
3. |
It occurs only in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. |
3. |
It occurs in the mesophyll and bundle-sheath cells of the leaves. |
|
4. |
It is a slower process of carbon fixation and photo-respiratory losses are high. |
4. |
It is a faster process of carbon fixation and photo-respiratory losses are low. |
|
5. |
Occurs in all the plants |
5. |
Occurs only in C4 plants |
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA plant in your garden avoids photorespiratory losses, has improved water use efficiency, shows high rate of photosynthesis at high temperatures and has improved efficiency of nitrogen utilisation. In which of the following physiological groups would you assign this plant?
C4
CAM
Nitogen-fixer
Nitogen-fixer
Emerson's enhancement effect and red drop have instrumental in the discovery of
two photosystems operating simultaneously
photophosphorylation and cyclic electron transport
oxidative phosphorylation
oxidative phosphorylation
Specialised epidermal cells surrounding the guard cells are called
sunbsidiary cells
bulliform cells
lenticels
lenticels
The three boxes in this diagram represent the three major biosynthetic pathways in aerobic net reactant or products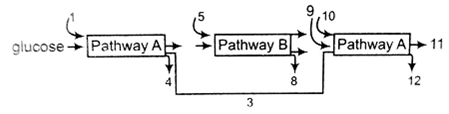
Arrows numbered 4, 8 and 12 can all be
NADH
ATP
H2O
H2O
