 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Describe the following giving linked chemical equations:
(i) Cannizzaro reaction
(ii) Decarboxylation
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) Cannizaro reaction
In this reaction, the aldehydes which do not have a -hydrogen atom, undergo self-oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with a concentrated alkali.
Example:

(ii) Decarboxylation
The decarboxylation reaction can be carried out either by using soda lime or by electrolysis
Using soda lime: Sodium salts of carboxylic acids when heated with soda lime (NaOH + CaO) in the ratio 3:1) undergo decarboxylation reaction to yield alkanes.
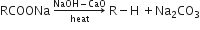
Electrolytic decarboxylation: Electrolysis of aqueous solutions of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acids give alkanes having twice the number of carbon atoms present in the alkyl group of acid.
This is known as Kolbe’s decarboxylation.
2RCOONa--> 2RCOO- + 2Na+
H2O-->2OH- + 2H+
At Anode:-
2RCOO- - 2e---> CO2 + R - R
At Cathode:-
2H+ + 2e----> H2
b)
A compound 'A' of molecular formula C2H3OCl undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C and D in the following reactions:
![]()
(b) Distinguish between the following:
(i) C6H5-COCH3 and C6H5 - CHO
(ii) Benzoic acid and methyl benzoate
(c) Write the structure of 2- methylbutanal.
(a) Write the structures of the main product when acetone ( CH3-CO-CH3) reacts with the following reagent:
(i) Zn-Hg/conc. HCl
(ii) H2N-NHCONH2/H+
(iii) CH3MgBr and then H3O+
(a) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point:
C2H5OH, CH3-CHO, CH3-COOH
(b) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
CH3CH2CHO and CH3CH2COCH3
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer - Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson’s ether synthesis
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) How will you convert the following?
(i) Propanone to Propan-2-ol
(ii) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy propanoic acid
(iii) Toluene to benzoic acid
(b) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between:
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(ii) Ethanal and Propanal
(a) Write the products of the following reactions:
(b) Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
(i) F — CH2 —COOH or Cl — CH2 — COOH
(ii) 
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Write a suitable chemical equation to complete each of the following transformations:
(i) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
(ii) 4-methylacetophenone to benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Propanol and propanone
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their property as indicated:
(i) Acetaldeyde, Acetone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(ii) Benzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength).
(iii) CH3CH2CH (Br) COOH, CH3CH (Br) CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH (acid strength)
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions:
Or
(a)Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in Cannizzaro reaction.
(b)Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(c)Why pKa of F-CH2-COOH is lower than that of Cl−CH2−COOH?
(d)Write the product in the following reaction:
(e)How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone?
