 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Typei) Mn Shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4.
ii) Cr2+ is a strong reducing agent.
iii) Cu2+ salts are coloured while Zn2+ salts are white.
b) Complete the following equations: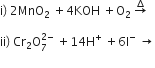
i) Mn Shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine, it shows the highest oxidation state of +4 because of the ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds with Mn metal.
ii) Cr2+ is strongly reducing in nature. It has a d4 configuration. Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent because it can lose one of its electrons to become Cr3+ in which the t2g level of d-orbital is half filled and the eg level is empty which is a more stable configuration.
iii) The electronic configuration of Zn = 3d10 4s2
Zn2+ = 3d10
where as the electronic configuration of Cu = 3d10 4s1
Cu2+ =3d9
In the case of Zn fully filled d orbital is present therefore no d-d transition can be possible in this case and it is colourless.
In the case of copper 3d9 because of d-d transition electrons emits light in the visible range and hence they are coloured compounds.
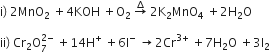
Distinguish between:
i) C6H5-COCH3 and C6H5-CHO
ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH
c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO,CH3COOH,CH3CH2OH
Or
a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff Kishner reduction.
b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
C6H5COCH3, CH3-CHO, CH3COCH3
c) why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group ?
d) Write the product in the following reaction![]()
e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomers B forms a yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeRearrange the compounds of each of the following sets in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 3-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutaneHow would you obtain the following?
(i) Benzoquinone from phenol
(ii) 2-methyl propan-2-ol from methyl-magnesium bromide
(iii) Propane-2-ol from propene
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
(b) How would you obtain the following?
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal
(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol
(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene
OR
(a) Given chemical tests to distinguish between the following:
(i) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following: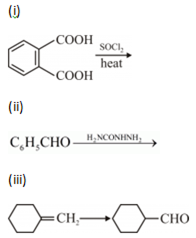
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents:
(i) HCN
(ii) H2N−OH
(iii) CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol
(ii) Propanal and Propanone
OR
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Cl−CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of the carbonyl group.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Rosenmund reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro's reaction
(c) Out of CH3CH2−CO−CH2−CH3 and CH3CH2−CH2−CO−CH3, which gives iodoform test?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDo the following conversions in not more than two steps :
Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
