 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange the following in the decreasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solutions:
CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3 N and NH3
(a) Complete the following chemical reactions equations:
(i) P4+SO2Cl2 -->
(ii) XeF6+H2O -->
(b) Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in each of the following cases:
(i) and the angle O - S - O
(ii) ClF3 and the angle F - Cl - F
(iii) XeF2 and the angle F - Xe - F
Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) NaOH+Cl2 -->
(ii) XeF4+O2F2--->
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) H3PO2
(ii) H2S2O7
(iii) XeOF4
State reasons for each of the following:
The N-O bond in is shorter than the N-O bond in
State reasons for each of the following:
(i) All the P-Cl bonds in PCl5 molecule are not equivalent.
(ii) Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound whereas NCl3 is not.
(ii) F2 is most reactive of all the four common halogens.
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) C + H2SO4 (conc.)-->
(ii) P4 + NaOH + H2O-->
(iii) Cl2+F2 ------>
(excess)
(i) As we move down the group 17, the size of the atom increases from fluorine to chlorine. The larger difference in the size of N and Cl results in the weakness of strength of N-Cl bond.
On the other hand, the difference in size of N and F is small; consequently, the N-F bond is quite strong. As a result, NF3 is an exothermic compound.
(ii)
1. F-F bond has low enthalpy because the fluorine atom has a small size and due to their small size, there is repulsion between two atoms making its bond enthalpy lower, hence more reactivity is more.
2. It has a small size and high charge density due to which it is the most electronegative element.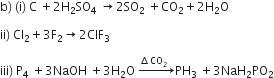
(a) Account for the following:
(i) The acidic strength decreases in the order HCl > H2S > PH3
(ii) Tendency to form pentahalides decreases down the group in group 15 of the periodic table.
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) P4 + SO2Cl2-->
(ii) XeF2 + H2O--->
(iii) I2+HNO3(conc.)--->
