 Short Answer Type
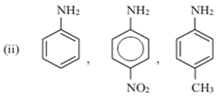
Short Answer TypeArrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength:
(i) C6H5 – NH2, C6H5 – CH2 – NH2, C6H5 – NH – CH3
Give reasons for the following:
(i) N2 is less reactive at room temperature.
(ii) H2Te is the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 16 elements.
(iii) Helium is used in diving apparatus as a diluent for oxygen.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Oxygen is a gas but sulphur is solid.
(ii) O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
(iii) BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 15 elements.
Explain the following facts giving appropriate reason in each case:
(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound whereas NCl3 is not.
(ii) All the bonds in SF4 are not equivalent.
(i) As we move down the group 17, the size of the atom increases from fluorine to chlorine. The instability of NCl3 is due to the weak NCl bond. This is due to the large difference in the size of nitrogen and chlorine atoms. On the other hand, atoms of both nitrogen (75 pm) and fluorine (72 pm) are small sized. Thus, bonding in NF3 is quite strong and it is an exothermic compound.
(ii)SF4 has four bonded atoms and one lone pair so SF4 has sp3d hydridisation and thus have trigonal bipyramid structure in which one axial position is occupied by a lone pair of electrons. This lone pair finds a position that minimizes the number of 900 repulsion it has with bonding electron pairs. This results in two types of angles.
Equatorial bond angle F - S - F° (LP-BP repulsion >BP – BP repulsion)
Axial bond angle F - S - F<90°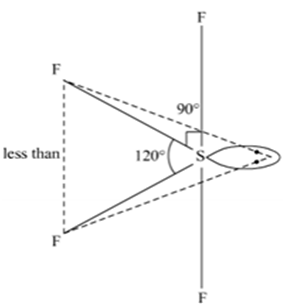
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Draw the molecular structure of the following compounds.
(i) N2O5
(ii) XeOF4
(b) Explain the following observation:
(i) Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.
(ii) ICI is more reactive than I2.
(iii) Despite the lower value of its electron gain enthalpy with a negative sign, fluorine (F2) is a stronger oxidizing agent than Cl2.
(a) Complete the following chemical equation
(i) Cu + HNO3 (dilute) --->
(ii) XeF4 + O2F2 -->
(b) Explain the following observation:
(i) Phosphorus has a greater tendency for catenation than nitrogen.
(ii) Oxygen is a gas but sulphur a solid.
(iii) The halogens are coloured. Why?
(a) Account for the following:
(i)Ozone is thermodynamically unstable.
(ii)Solid PCl5 is ionic in nature.
(iii)Fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF.
(b) Draw the structure of
(i) BrF5
(ii) XeF4
OR
(i)Compare the oxidizing action of F2 and Cl2 by considering parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy.
(ii)Write the conditions to maximize the yield of H2SO4 by contact process.
(iii)Arrange the following in the increasing order of property mentioned:
(a)H3PO3, H3PO4, H3PO2 (Reducing character)
(b)NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 (Base strength)
