 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeSolve theВ following initial value problem:
(1 + x y) y dx + (1 – x y) x dy = 0, y (1) = 1.
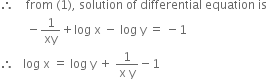
Solve the differential equation;
x (1 + y2В ) dx – y (1 + x2В ) dy = 0 В given that y = 0 when x = 1.В
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFind the equation of the curve passing through the point (1, 1) whose differentialВ equation is x dy = (2 x2В + 1) dx (x в‰ 0).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type