297.
Find the equation of a curve passing through the origin given that the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point (x, y) is equal to the sum of the coordinates of the point.
Let y = f (x) be the equation of curve.
We know that 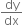 represents the slope of the tangent
represents the slope of the tangent to the curve at the point (x, y).
From the given condition.
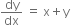
or
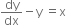
Comparing
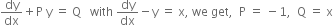
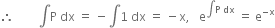
Solution of differential equation is

or
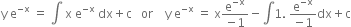
or
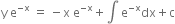
or

or
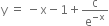
or
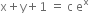
...(1)
Now curve passes through origin (0, 0).

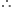
from (1),
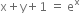
is the required equation of curve.
74 Views
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions