 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAcetone is treated with an excess of ethanol in the presence of hydrochloric acid. The product obtained is.
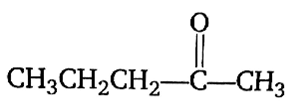
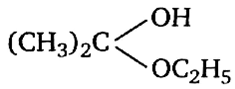
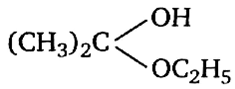
The correct order of decreasing acid strength of trichloroacetic acid (A), trifluoroacetic acid (B), acetic acid (C) and formic acid (D) is
B > A> D > C
B > D > C > A
A> B > C > D
A> B > C > D
Which of the following compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali?
Acetophenone
Methyl acetate
Acetamide
Acetamide
Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried out in the presence of which of the following?
Zn -Hg with HCl
LiAlH4
H2 and Pt as catalyst
H2 and Pt as catalyst
In a set of reactions, m-Bromo benzoic acid g ave a product D. Identify the product D. 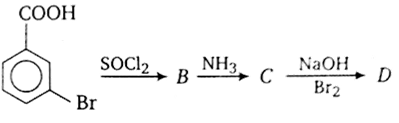
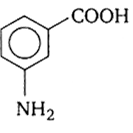
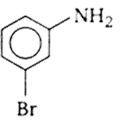
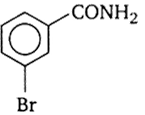

A reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by the elimination of water. The reagents is
a Grignard reagent
hydrazine in presence of feebly acidic solution
hydrocyanic acid
hydrocyanic acid
Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily?
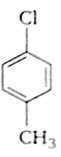
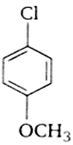

Match the compounds given in the list I with List II and select the suitable option using the code given below.
|
|
List I |
|
List II |
|
A. |
Benzaldehyde |
1. |
Phenolphtalein |
|
B. |
Phthalic anhydride |
2. |
Benzoin Condensation |
|
C. |
Phenyl benzoate |
3. |
Oil of wintergreen |
|
D. |
Methyl salicylate |
4. |
Fries rearrangement |
|
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
|
4
|
1
|
3
|
2
|
|
A
|
B | C | D |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
|
A
|
B | C | D |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
|
A
|
B | C | D |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
D.
|
A
|
B | C | D |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
A. Benzoin condensation: When an ethanolic solution of benzaldehyde is heated with a strong alkali like KCN or NaCN, we get benzoin.
B. Formation of Phenolphthalein: When phenol is treated with a pthalic anhydride in the presence of concentrated H2SO4, it gives phenolphthalein, an indicator.
C. Fries rearrangement: When phenyl benzoate heated with anhydrous AlCl3 in the presence of inert solvent gives ortho and para - hydroxy benzophenone. In this rearrangement, there is a benzoyl group migration from the phenolic oxygen to an ortho and para - position.
D. Methyl salicylate: A chief constituent of oil of wintergreen
