 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn the following reaction,  the product 'X' is
the product 'X' is
C6H5CH2OCH2C6H5
C6H5CH2OH
C6H5CH3
C6H5CH3
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction?
RX + KOH → ROH + KX
2RX + 2Na → R- R
RX + H2 → RH + HX
RX + H2 → RH + HX
Consider the following reaction,
the product Z, is
CH2 = CH2
CH3CH2-O-CH2-CH3
CH3-CH2-O-SO3H
CH3-CH2-O-SO3H
Benzene reacts with CH3Cl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to form
toluene
chlorobenzene
benzylchloride
benzylchloride
In an SN2 substitution reaction of the type which ![]() one of the followings has the highest relative rate?
one of the followings has the highest relative rate?
CH3-CH2-CH2Br
CH3-CH(CH2)-CH2Br
CH3C(CH3)2CH2Br
CH3CH2Br
D.
CH3CH2Br
The relative reactivity of alkyl halide towards SN N reactions is as follows;
Primary > secondary > Tertiary
However, if the primary alkyl halide or the nucleophile/base is sterically hindered the nucleophile will have difficulty to getting the back side of the alpha carbon as a result of this elimination product will be predominant. Here CH3CH2Br is the least hindered, hence it has the highest relative rate towards SN2 reaction.
Consider the following compounds: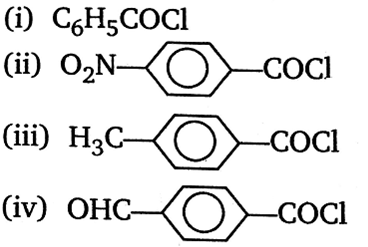
The correct decreasing order of their reactivity towards hydrolysis is;
(ii) >(iv) > (iii) > (i)
(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
(iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
(iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
Ethylene oxide when treated with Grignard reagent yields:
Secondary alcohol
tertiary alcohol
cyclopropyl alcohol
cyclopropyl alcohol
