 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Define molar conductivity of a solution and explain how molar conductivity changes with a change in concentration of solution for a weak and a strong electrolyte.
(b) The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is Ω 1500 . What is the cell constant if the conductivity of 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.146x10-3 S cm-1?
(a) Complete the following chemical reactions equations:
(i) P4+SO2Cl2 -->
(ii) XeF6+H2O -->
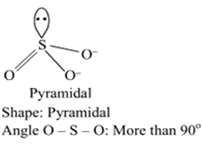
(b) Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in each of the following cases:
(i) and the angle O - S - O
(ii) ClF3 and the angle F - Cl - F
(iii) XeF2 and the angle F - Xe - F
(i) P4+ 10SO2Cl2 ---> 4 PCl5+ 10SO2
(ii) Equation for complete hydrolysis:
XeF6+H2O ---->XeO3+6HF
Equations for partial hydrolysis
XeF6+H2O ---> XeOF3+2HF
XeF6+2H2O ---> XeO2F2+4HF
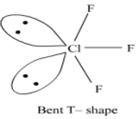
Angle F – Cl - F: Less than90o
iii) 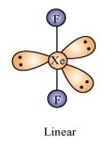
Angle F- Xe- F 80o
Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) NaOH+Cl2 -->
(ii) XeF4+O2F2--->
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) H3PO2
(ii) H2S2O7
(iii) XeOF4
Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions: ethanol, propanal, propanone, butanone.
Write any two reactions of glucose which cannot be explained by the open chain structure of glucose molecule.
Draw the structure of the monomer for each of the following polymers:
(i) Nylon 6
(ii) Polypropene
