 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain “large number of buyers and sellers” features of a perfectly competitive market.
Production in an economy is below its potential due to unemployment. Government starts employment generation schemes. Explain its effect using production possibilities curve.
As initially, the production in the economy is below its potential due to unemployment, this suggests that the economy is operating at a point below the Production Possibility curve (PPC). As the government starts employment generation schemes, the unemployed resources get utilised. In a situation of full employment the economy would move to a point on the PPC.
Consider the example of the economy producing two goods- consumer goods and capital goods. Suppose AB is the Production Possibility Curve (PPC) depicting full-employment of resources.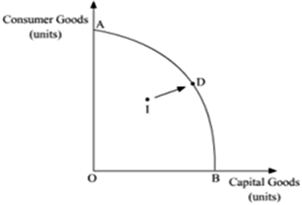
Initially, suppose the economy is at point I (which is below the PPC) where, the economy is below the potential level. As employment in the economy rises, the economy starts moving at a point towards the PPC. At full employment, it will reach a point on the PPC such as point D.
Explain the conditions of producer’s equilibrium with the help of a numerical example.
The price elasticity of demand for a good is − 0.4. If its price increases by 5 percentage, by what percentage will its demand fall? Calculate.
Explain any two factors that affect the price elasticity of demand. Give suitable examples.
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false.
A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the Law of Variables Proportions with the help of total product and marginal product curves.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain the relationship between prices of other goods and demand for the given period.
