 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Define electric dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector? Derive the expression for the electric field of a dipole at a point on the equatorial plane of the dipole.
(b) Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero.
Using Gauss’ laws deduce the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged spherical conducting shell of radius R at a point (i) outside and (ii) inside the shell.
Plot a graph showing variation of electric field as a function of r > R and r < R. (r being the distance from the centre of the shell).
i) Consider a uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R carrying charge Q. To find the electric field outside the shell, we consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius (r >R), concentric with given shell. If E is electric field outside the shell, then by symmetry electric field strength has same magnitude E0 on the Gaussian surface and is directed radially outward.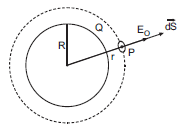
So, electric flux through Gaussian surface is given by, ![]()
Therefore, ![]()
Charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is Q.
Therefore, using gauss’s theorem, we have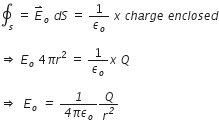
Thus, electric field outside a charged thin spherical shell is the same as if the whole charge Q is concentrated at the centre.
ii) Electric field inside the shell: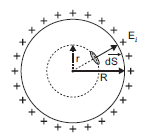
The charge resides on the surface of a conductor. Thus, a hollow charged conductor is equivalent to a charged spherical shell. Let’s consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius (r < R). If E is the electric field inside the shell, then by symmetry electric field strength has the same magnitude Ei on the Gaussian surface and is directed radially outward.
Electric flux through the Gaussian surface is given by, ![]()
= ![]()
Now, Gaussian surface is inside the given charged shell, so charge enclosed by Gaussian surface is zero.
Therefore, using Gauss’s theorem, we have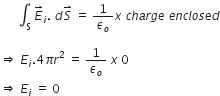
Thus, electric field at each point inside a charged thin spherical shell is zero.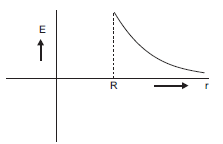
The graph above shows the variation of electric field as a function of R.
Using Bohr’s postulates, derive the expression for the frequency of radiation emitted when electron in hydrogen atom undergoes transition from higher energy state (quantum number ni ) to the lower state, (nf ).
When electron in hydrogen atom jumps from energy state ni =4 to nf =3, 2, 1, identify the spectral series to which the emission lines belong.
(a) Draw the plot of binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) as a function of mass number A. Write two important conclusions that can be drawn regarding the nature of nuclear force.
(b) Use this graph to explain the release of energy in both the processes of nuclear fusion and fission.
(c) Write the basic nuclear process of neutron undergoing –decay. Why is the detection of neutrinos found very difficult?
