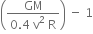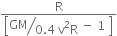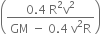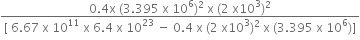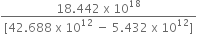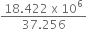A rocket is fired ‘vertically’ from the surface of mars with a speed of 2 km s–1. If 20% of its initial energy is lost due to Martian atmospheric resistance, how far will the rocket go from the surface of mars before returning to it? Mass of mars = 6.4× 1023 kg; radius of mars = 3395 km; G = 6.67× 10-11 N m2 kg–2.
219 Views

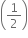 mv2
mv2 
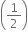 mv2 -
mv2 - 



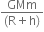
 =
= 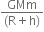
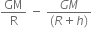
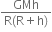
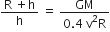
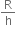 =
=