 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhen a stimulus is applied at a site A on the polarised membrane, the membrane at the site A becomes freely permeable to Na+ leading to rapid influx of Na+ followed by the reversal of the polarity at that site. The outer surface of the membrane becomes negatively charged and
the inner side becomes positively charged. The point A becomes depolarised.
The electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane at the site A is called the
action potential or termed as a nerve impulse. At other sites like point B, immediately ahead, the axon membrane has a positive charge
on the outer surface and a negative charge on its inner surface.
Because of this difference in polarity, the current flows on the inner surface from site A to site B. On the outer surface current flows from site B to site A to complete the circuit. Hence, the polarity at the site is reversed, and an action potential is generated at site B.
Thus, the impulse (action potential) generated at site A arrives at site B. The sequence is repeated
along the length of the axon and consequently the impulse is conducted.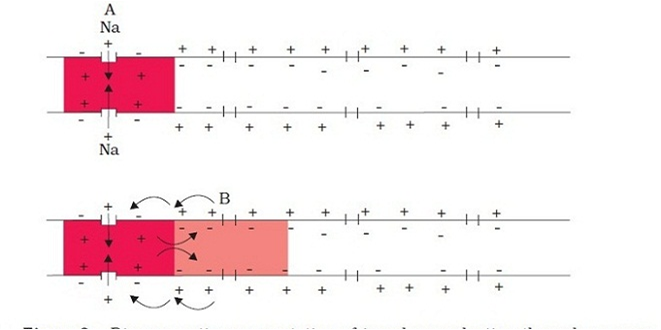
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type