 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn mammals, which blood vessel would normally carry largest amount of urea?
Dorsal aorta
Hepatic vein
Hepatic portal vein
Hepatic portal vein
The figure shows a human urinary system with structure labelled A to D. Select option, which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and of function.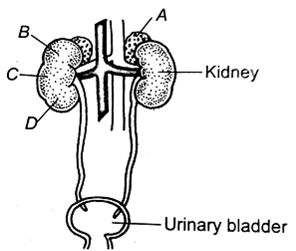
A - adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete catecholamines, which stimulate glycogen breakdown
B- pelvis -board funnel-shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle
C - mediulla-inner zone of kidney and contains complete nephrons.
C - mediulla-inner zone of kidney and contains complete nephrons.
Human urine is usually acidic because
The sodium transporter exchanges one hydrogen ion for each sodium ion, in peritubular capillaries.
Excreted plasma proteins are acidic
potassium and sodium exchange generates acidity
potassium and sodium exchange generates acidity
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70-80 percent from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron?
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
Distal convoluted tubule
Proximal convoluted tubule
Proximal convoluted tubule
Choose the correctly matched pair.
Inner Lining of salivary ducts - Ciliated epithelium
Moist surface of buccal cavity - Flandular epithelium
Tubular parts of nephrons - Cuboidal epithelium
Tubular parts of nephrons - Cuboidal epithelium
Which of the following causes an increase in sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule?
Increase in aldosterone levels
Increase in antidiuretic hormone levels
Decrease in aldosterone levels
Decrease in aldosterone levels
Which one of the following options gives the correct categorisation of six animals according to the type of nitrogenous wastes (A, B, C), they give out?
| A Ammonotelic |
B Ureotelic |
C Uricotelic |
| Pigeon, Humans | Aquatic Amphibia, Lizards | Cockroach, Frog |
| A Ammonotelic |
B Ureotelic |
C Uricotelic |
| Frog, Lizards | Aquatic Amphibia, Humans | Cockroach, Pigeon |
| A Ammonotelic |
B Ureotelic |
C Uricotelic |
| Aquatic Amphibia | Frog, Humans | Pigeon, Lizards, Cockroach |
| A Ammonotelic |
B Ureotelic |
C Uricotelic |
| Aquatic Amphibia | Frog, Humans | Pigeon, Lizards, Cockroach |
A fall in glomeruclar filtration rat (GFR) activates
Juxtra glomerular cells to release renin
Adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
Adrenal medulla to release adrenaline
Adrenal medulla to release adrenaline
Which one of the following characteristics is common both in humans and adult frogs?
Four chambered heart
Internal fertilisation
Nucleated RBCs
Nucleated RBCs
Removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron will result in
more diluted urine
no change in quality and quantity of urine
no change in quality and quantity of urine
A.
more diluted urine
The removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron results in lack of reabsorption of high threshold substance from renal tubules and obligatory reabsorption of water is also affected leading to more diluted urine. Since, proximal convoluted tubule is mainly associated with reabsorption of much water by osmosis, reabsorption of glucose and amino acids by secondary active transport and other salts and ions as Na+, K+, vitamins act by primary active transport.
