Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Define the terms osmosis and osmotic pressure. Is the osmotic pressure of a solution a colligative property? Explain.
(b) Calculate the boiling point of a solution prepared by adding 15.00 g of NaCl to 250.0 g of water. (Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol-1), (Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g)
(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound whereas NCl3 is not.
(ii) F2 is most reactive of all the four common halogens.
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) C + H2SO4 (conc.)-->
(ii) P4 + NaOH + H2O-->
(iii) Cl2+F2 ------>
(excess)
(a) Account for the following:
(i) The acidic strength decreases in the order HCl > H2S > PH3
(ii) Tendency to form pentahalides decreases down the group in group 15 of the periodic table.
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) P4 + SO2Cl2-->
(ii) XeF2 + H2O--->
(iii) I2+HNO3(conc.)--->
Answer the following:
(i) Haloalkanes easily dissolve in organic solvents, why?
(ii) What is known as a racemic mixture? Give an example.
(iii) Of the two Bromo derivatives, C6H5CH(CH3)Br and C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, which one is more reactive in Sn1 substitution reaction and why?
i) Haloalkanes can easily dissolve in organic solvents of low polarity because the new forces of attraction set up between haloalkanes and the solvent molecules are of same strength as the forces of attraction being broken.
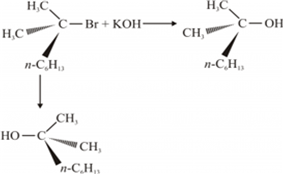
(ii) A mixture of equal amounts of two enantiomers is known as racemic mixture. For example: When a 3° halide undergoes substitution with KOH, the reaction proceeds through SN 1 mechanism forming the racemic mixture in which one of the products has the same configuration as a reactant, while the other product has an inverted configuration.
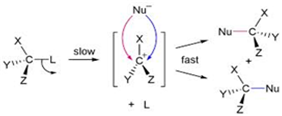
(iii) In SN1 reaction mechanism leads through the carbocation pathway.
More stable the carbocation, more reactive will be substrate .the carbocation formed by two compounds are as follows:
Compound (C6H5)2CHBr = carbocation (C6H5)2CH+
Compound C6H5CH(CH3)Br=carbocation C6H5(CH3)CH+
Out of these two carbocations (C6H5)2CH+ is more stable than C6H5(CH3)CH+ because the carbocation(C6H5)2CH+ is resonance stabilised by two benzene rings .therefore (C6H5)2CHBr is more reactive than C6H5CH(CH3)Br. Resonance stabilisation of carbocation with one benzene ring is shown :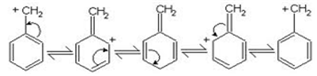
Describe the following giving one example for each:
(i) Detergents
(ii) Food preservatives
(iii) Antacids
Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Propanal and propanone,
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone.
(b) How would you obtain
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal,
(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol,
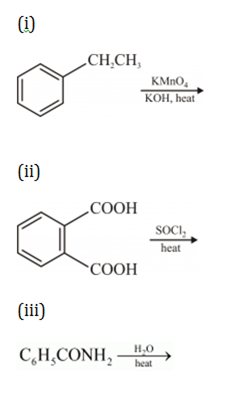
(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene?
(a) Describe the following giving linked chemical equations:
(i) Cannizzaro reaction
(ii) Decarboxylation
(b) Complete the following chemical equations: