 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Define the following terms:
(i) Ideal solution
(ii) Azeotrope
(iii) Osmotic pressure
(b) A solution of glucose (C6H12O6) in water is labeled as 10% by weight. What would be the molality of the solution?
(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol-1)
(a) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Mn3+ is a good oxidising agent.
(ii) ![]() Values are not regular for first row transition metals (3d series).
Values are not regular for first row transition metals (3d series).
(iii) Although ‘F’ is more electronegative than ‘O’, the highest Mn fluoride is MnF4, whereas the highest oxide is Mn2O7.
(b) Complete the following equations:
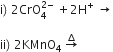
(a) Why do transition elements show variable oxidation states?
(i) Name the element showing the maximum number of oxidation states among the first series of transition metals from Sc (Z = 21) to Zn (Z = 30).
(ii) Name the element which shows only +3 oxidation state.
(b) What is lanthanoid contraction? Name an important alloy which contains some of the lanthanoid metals.
(a) How will you convert the following?
(i) Propanone to Propan-2-ol
(ii) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy propanoic acid
(iii) Toluene to benzoic acid
(b) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between:
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(ii) Ethanal and Propanal
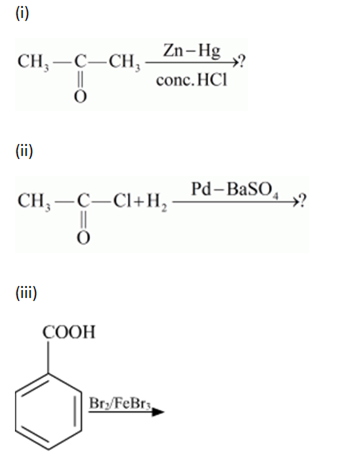
(a) Write the products of the following reactions:
(b) Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
(i) F — CH2 —COOH or Cl — CH2 — COOH
(ii) 
(a)
(i)![]()
This reaction is Clemmensen reduction.
(ii)
This reaction is Rosenmunds reduction.
(iii)
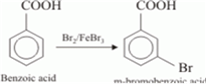
This reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
(b)
(i) F — CH2 — COOH is a stronger acid than Cl — CH2 — COOH because F is more electronegative than Cl so it will favour the release of H+ ion faster by dragging the electron density towards itself more as compared to Cl.
(ii) Acetic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. On losing a proton, carboxylic acid forms carboxylate ion and phenol forms phenoxide ion. The negative charge is delocalized in both the molecules. The conjugate base of the carboxylic acid has two resonance structures (shown below) in which negative charge is delocalized over two oxygen atoms which stabilizes the carboxylate ion.
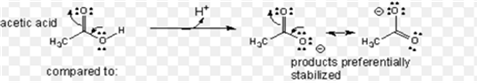
On the other hand, in phenoxide ion, the negative charge is delocalized over entire molecule on the less electronegative carbon atom as given below.
Thus resonance in phenoxide is not important as compared to resonance in carboxylate ion.
Further, in carboxylate ion, the negative charge is effectively delocalized over two oxygen atoms whereas it is less effectively delocalized over one oxygen atom and the less electronegative carbon atom in phenoxide ion.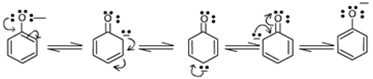
Thus acetic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
