 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322 ? Mention the role they play.
(b) Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme 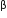 -galactosidase a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above ?
-galactosidase a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above ?
Suggest and describe a technique to obtain multiple copies of a gene of interest in vitro.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeA. Describe the characteristics a cloning vector must possess.
B. Why DNA cannot pass through the cell membrane? Explain. How is a bacterial cell made competent to take up recombinant DNA from the medium?
If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some experiments, explain the process of the following:
(i) Cutting this desired gene at specific location
(ii) Synthesis of multiple copies of this desired gene
I. Restriction enzymes - Cutting of the desired gene at a specific location is attained by using restriction endonucleases. These enzymes are specialised to cut the fragment of DNA at specific locations. Each restriction endonuclease functions by ‘inspecting’ the length of a DNA sequence. Once it finds its specific recognition sequence, it binds to the DNA and cuts each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in their sugar -phosphate backbones. Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence (sequence of base pairs that reads same on the two strands when the orientation of reading is kept the same) in the DNA. Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands. This leaves single-stranded portions at the ends.
II. Polymerase Chain Reaction - PCR is used to create multiple copies of the DNA being incorporated with molecular biology tools to obtain a higher copy of the desired gene. Two sets of chemically synthesised oligonucleotides and DNA polymerase are being used in vitro for the multiplication of the desired gene.
The PCR produces approximately billion copies of a gene in less than 20 minutes. Such higher number of the product is achieved by use of thermostable DNA polymerase (isolated from a bacterium, Thermus aquaticus.
Components used during PCR - Template DNA, DNA polymerase, Primers and buffer.
Steps of PCR – •
Denaturation - The DNA is denatured that is the strands are separated by heating the dsDNA to 95-degree celsius. This breaks hydrogen bonds that hold DNA strands together in the helix. •
Annealing- The mixture is cooled, this allows the primer to bind to their respective complementary sequence. •
Extension- The mixture is then heated so that DNA polymerase can synthesise new strands.
The whole cycle is repeated to create multiple copies.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type