 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples.
Define 'Market-supply'. What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government imposes a tax on the production of that good? Explain.
What is a supply schedule? What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government gives a subsidy on the production of that good? Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is meant by producer's equilibrium? Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium through the 'total revenue and total cost' approach. Use diagram.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an 'increase' in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy is a production possibilities curve concave? Explain.
Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is concave to the origin because of the increasing opportunity cost. As we move down along the PPC, to produce each additional unit of one good, more and more units of other good need to be sacrificed. That is, as we move down along the PPC, the opportunity cost increases. And this causes the concave shape of PPC.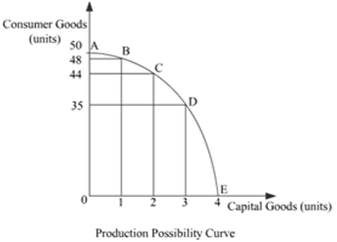
In the above graph, AE represents the PPC for capital goods and consumer goods. Suppose the initial production point is B, where 1 unit of capital goods and 48 units of consumer goods are produced. To produce one additional unit of capital good, 4 units of consumer good must be sacrificed (point c). Thus at point c, the opportunity cost of one additional capital good is 4 units of consumer goods. On the other hand, at point D, the opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of capital good is 9 units of consumer goods. Thus, as we move down the PPC from point C to point D, the opportunity cost increases. This confirms the concave shape of PPC.
