 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples.
Define 'Market-supply'. What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government imposes a tax on the production of that good? Explain.
What is a supply schedule? What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government gives a subsidy on the production of that good? Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is meant by producer's equilibrium? Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium through the 'total revenue and total cost' approach. Use diagram.
Explain the three properties of indifference curves.
The properties of indifference curves are as follows:
(1) Indifference curves slope downward to the right:
This property implies that an indifference curve has a negative slope. If the preferences are monotonic, an increase in the amount of good 1. along the indifference curve is associated with a decrease in the amount of good 2. This implies that the slope of the indifference curve is negative. Thus, monotonicity of preferences implies that the indifference curves are downward sloping to the right.
(2) Indifference curves are convex to the origin:
Another important property of indifference curves is that they are usually convex to the origin.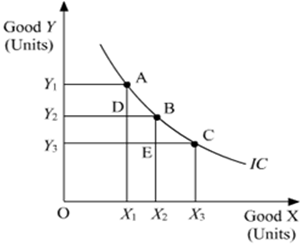
In other words, the indifference curve is relatively flatter in its right hand portion and relatively steeper in its left hand portion. This is because as the consumers consumes more and more of one good, the marginal utility good fall. In other words, the consumer is willing to sacrifice less and less for each additional unit of the other good consumed. Thus, as we move down the IC, MRS diminishes. This suggests the convex shape of indifference curve.
(3) Slope of IC: The Slope of an IC is given by the Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS). Marginal rate of substitution refers to the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for each additional unit of the other good.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an 'increase' in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type