 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples.
Define 'Market-supply'. What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government imposes a tax on the production of that good? Explain.
What is a supply schedule? What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government gives a subsidy on the production of that good? Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is meant by producer's equilibrium? Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium through the 'total revenue and total cost' approach. Use diagram.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an 'increase' in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
An equilibrium is defined as a situation where the plans of all consumers and firms in the market match and the market clears. When the supply and demand curves intersect, the market is in equilibrium. This is where the quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. The corresponding price is the equilibrium price or market-clearing price, the quantity is the equilibrium quantity.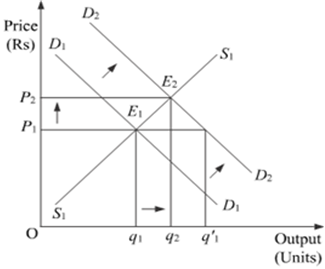
Suppose D1 and S1 are the initial market demand curve and the initial market supply curve, respectively. The initial equilibrium is established at point E1, where the market demand curve and the market supply curve intersects each other. Accordingly, the equilibrium price is OP1 and the equilibrium quantity demanded is Oq1.
Now, if there is an increase in the market demand, the market demand curve shifts parallelly rightwards to D2 from D1, while the market supply curve remains unchanged at S1. This implies that at the initial price OP1, there exist excess demand equivalent to (Oq'1 - Oq1) units. This excess demand will increase competition among the buyers and they will now be ready to pay a higher price to acquire more units of the good. This will further raise the market price. The price will continue to rise till it reaches OP2. The new equilibrium is established at point E2, where the new demand curve D2 intersects the supply curve S1
Hence, an increase in demand with supply remaining constant, results in rise in the equilibrium price as well as the equilibrium quantity.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type