 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples.
Define 'Market-supply'. What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government imposes a tax on the production of that good? Explain.
What is a supply schedule? What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government gives a subsidy on the production of that good? Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is meant by producer's equilibrium? Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium through the 'total revenue and total cost' approach. Use diagram.
Equilibrium refers to a state of rest when no change is required. A firm (producer) is said to be in equilibrium when it has no inclination to expand or to contract its output. This state either reflects maximum profits or minimum losses.
There are two methods for determination of Producer’s Equilibrium:
1. Total Revenue and Total Cost Approach (TR-TC Approach)
2. Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost Approach (MR-MC Approach)
Under TR-TC Approach, A firm attains the stage of equilibrium when it maximises its profits, i.e. when he maximises the difference between TR and TC. After reaching such a position, there will be no incentive for the producer to increase or decrease the output and the producer will be said to be at equilibrium.
According to TR-TC approach, producer’s equilibrium refers to stage of that output level at which the difference between TR and TC is positively maximized and total profits fall as more units of output are produced.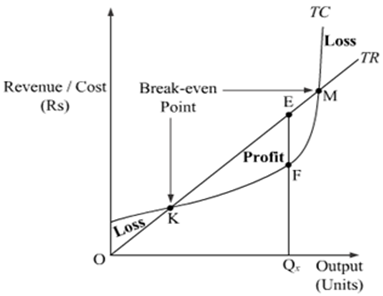
So, Two essential conditions for producer’s equilibrium are:
(i) The difference between TR and TC is positively maximized;
(ii) Total profits fall after that level of output.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an 'increase' in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type